Tyrosyl-DNA Phosphodiesterase I a critical survival factor for neuronal development and homeostasis
Robert C.A.M. van Waardenburg*
Abstract
Tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase I (TDP1), like most DNA repair associated proteins, is not essential for cell viability. However, dysfunctioning TDP1 or ATM (ataxia telangiectasia mutated) results in autosomal recessive neuropathology with similar phenotypes, including cerebellar atrophy. Dual inactivation of TDP1 and ATM causes synthetic lethality. A TDP1H493R catalytic mutant is associated with spinocerebellar ataxia with axonal neuropathy (SCAN1), and stabilizes the TDP1 catalytic obligatory enzyme-DNA covalent complex. The ATM kinase activates proteins early on in response to DNA damage. Tdp1-/- and Atm-/- mice exhibit accumulation of DNA topoisomerase I-DNA covalent complexes (TOPO1-cc) explicitly in neuronal tissue during development. TDP1 resolves 3’- and 5’-DNA adducts including trapped TOPO1-cc and TOPO1 protease resistant peptide-DNA complex. ATM appears to regulate the response to TOPO1-cc via a noncanonical function by regulating SUMO/ubiquitin-mediated TOPO1 degradation. In conclusion, TDP1 and ATM are critical factors for neuronal cell viability via two independent but cooperative pathways.
Tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase I (TDP1), a eukaryotic DNA repair enzyme that belongs to the phospholipase D super family1-3, is ubiquitously expressed in most if not all human and mouse tissue, from neurons to peripheral skeletal cells4. In the cell, TDP1 is detected in the nuclear-, cytosolic- and mitochondrial-compartments4,5. TDP1 is able to resolve a wide variety of phospho-adducts from the 3’ and 5’ ends of nicked DNA strands. Tdp1 substrates vary from small adducts, such as oxidative DNA damage and chain terminating nucleotides, to large adducts including potentially lethal protein-DNA covalent complexes or the protease-resistant peptides that are still covalently linked to the DNA after degradation6,7. Protein-DNA adducts include DNA topoisomerases (TOPOs) covalently linked to the DNA via a 3’phospho-tyrosyl or 5’phospho-tyrosyl linkage, representing a TOPO1-DNA (TOPO1-cc) or TOPO2-/TOPO3-DNA covalent complex, respectively8-10. In addition, TDP1 is able to hydrolyze a 3’phospho-histidyl linkage or TDP1 covalently bound to the DNA (TDP1-cc)11-13. Note: higher eukaryotic cells contain an additional enzyme called TDP2/TTRAP that resolves the 5’phospho-tyrosyl linkages more efficiently then TDP114-17. However, this enzyme is absent in yeast cells in which TDP1 resolved both 3’ and 5’phospho-tyrosyl linkages18.
To resolve this eclectic array of phospho-adducts, TDP1 utilizes the coordinated action of two catalytic histidines (Figure 1). In the case of hydrolyzing a 3’phospho-tyrosyl linkage, the N-terminally located histidine functions as a nucleophile (Hisnuc; His263 in human (h)Tdp1 and His182 in yeast (y)Tdp1) to attack the 3’phospho-tyrosyl linkage to form a 3’phospho-hystidyl bond. The C-terminally located histidine acts as a general acid/base (Hisgab; His493 in hTdp1 and His432 in yTdp1) that activates a water molecule to hydrolyze the Tdp1-DNA linkage formed in the first step, resulting in separation of Tdp1 from the DNA1,2,11,19.
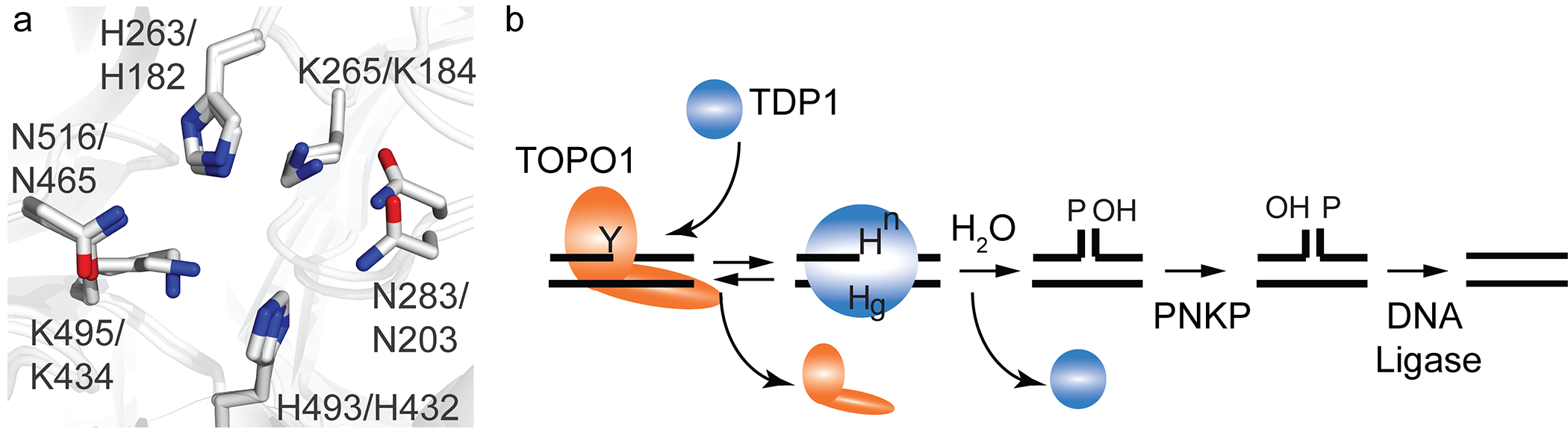
Figure 1: The TDP1 catalytic pocket and mechanism is conserved from yeast to human. (a) Overlay of the crystal structure catalytic pockets of yeast and human Tdp1 showing the two catalytic HxKxnN-motifs; H263,K265,N283 N-terminal motif and H493,K495,N516 C-terminal motif in human TDP1. H182,K185,N203 N-terminal motif and H432,K435,N434 C-terminal motif in yeast TDP1. Residues H263 in human TDP1 and H182 of yeast TDP1 represent the nucleophilic histidine (Hisnuc), while H493 of human TDP1 and H432 in yeast TDP1 represent the general acid/base histidine (Hisgab). [human TDP1; PDB # 1NOP46 and yeast TDP1; PDB# 1Q32]11. (b) Tdp1 catalytic of DNA topoisomerase I-DNA covalent complexes (TOPO1-cc); Tdp1 resolves the 3’phospho-tyrosyl linkage (Y) via nucleophilic attack of the Hisnuc (Hn), that releases TOPO1. This step generates the obligatory TDP1-DNA intermediate via 3’phospho-amide linkage. Water is activated by Hisgab (Hg) to hydrolyze the TDP1-DNA linkage allowing TDP1 to dissociate from the DNA. The exciting single-strand nick requires further processing by polynucleotide kinase-phosphatase (PNKP) prior to DNA ligation.
A substitution of the hTdp1Hisgab to Arginine (hTdp1H493R) has been identified as the molecular basis for the rare autosomal recessive neurodegenerative disease Spinocerebellar Ataxia with Axonal Neuropathy or SCAN113. SCAN1 symptoms are similar to Ataxia Telangiectasia (A-T) and Ataxia with Oculomoter Apraxia (AOA1). A-T results from defects in the serine/threonine protein kinase, DNA damage response regulator ATM (ataxia telangiectasia mutated20, and AOA1 is caused by a defect in the DNA repair enzyme aprataxin (APTX)21, respectively13,22. ATM is activated in response to the detection of double-strand breaks via the Mre11-Rad50-Nsb1 (MRN) complex to phosphorylate a plethora of downstream proteins, including H2AX and p5323,24. On the other hand, APTX is an adenyl-hydrolase that resolves 5’adenylated-DNA (5’AMP-DNA) adducts as a result of abortive DNA ligase activity21,25. The importance of DNA “end-processing” enzyme activities became even more evident with the observation that mutations in the kinase domain of polynucleotide kinase phosphatase (PNKP) are associated with AOA4, while other substitution in PNKP are detected in patients with microcephaly with seizures (MCSZ) (26-28). Moreover, loss of TDP2 activity is associated with autosome recessive spinocerebellar ataxia-23 or SCAR-2329,30.
SCAN1 patients demonstrate a progressive cerebellar atrophy that results in ataxia symptoms during late childhood (13-15 years). Intriguingly, this atrophy only seems to affect the cerebellar neurons within the vermis region of the cerebellum13,22. Moreover, these patients do not show an increase in cancer predisposition, immunodeficiencies, or cardiomyopathy. Takashima and colleagues originally proposed that the H493R substitution would inactivate the enzyme13; however, subsequent biochemical studies revealed a decreased dissociation rate resulting in an increased level of TDP1SCAN1-cc (Figure 1)31,33. Moreover, the only available resolved crystal structure of a Tdp1HisgabArg mutant enzyme is the yeast analogous substitution (yTdp1H432R)32. The yTdp1H432R crystal structure demonstrated that the arginine side chain reduces the depth of the TDP1 catalytic pocket, potentially obstructing a water molecule to enter the pocket at the correct position32. On the other hand, arginine is also a weaker general acid/base than histidine, which affects the activation rate of the water molecule that facilitates dissociation of Tdp1 from the DNA. Additionally, the arginine guanidinium moiety changes the electrostatic charge distribution within the catalytic pocket to highly positive32. All these factors contribute to the reduced dissociation rate of TDP1HisgabArg from the DNA. The biochemical/biophysical characteristics of the Hisgabgab substitution as well as the mild cellular toxicity induced by expression of this TDP1 HgabR-mutant are conserved between yeast and human TDP111,31-33. Moreover, examination of additional substitutions of the Hisgab/432 in yTdp1 showed that a His432Lys substitution resulted in a minor (~10-fold) decrease in catalytic activity with no detectable toxicity32. Conversely, expression of His432 substitution with residues that contain a smaller polar or aliphatic side chain such as Asn, Glu, Ser, Thr, Leu, Val and Ala, displays an acute toxicity, albeit recessive to wild type Tdp1. These observations also revealed that the SCAN1 mutation (HisgabArg) among the toxic Hisgab mutants exhibits only a mildly toxic phenotype. Similar to the SCAN1 mutant, the toxicity induced by expression of the HisgabAsn mutant is correlated with increased cellular levels of enzyme-DNA intermediates and a reduction in catalytic activity in both yeast and human TDP111,31-34[Cuya, van Waardenburg manuscript under revision Oncotarget]. It is therefore intriguing that more TDP1 single nucleotide polymorphisms are not identified and associated with neuronal syndromes or other diseases associated with genome instability etiology. Although substitution of either catalytic histidine results in a gain of function (toxicity and reduced activity)11,32,34, two questions remain open: How does the Tdp1H493R mutant enzyme cause the SCAN1 pathology? and Why are (cerebellar) neurons so sensitive to this toxic Tdp1 mutant?
Tdp1, like most DNA repair proteins/enzymes, is not essential for eukaryotic cell viability. This is generally due to the existence of redundant DNA repair processes that are able to resolve protein-DNA adducts. However, some human carcinomas developed a dependency on/or addiction of Tdp1 expression35,36. Currently, no mouse model for SCAN1 that expresses the HisgabArg substitution has been generated. However, three different groups generated a Tdp1 knockout mouse37-39. Interestingly, Tdp1-/- mice do not develop any ataxia or neuropathy symptoms related with SCAN1 or other behavioral phenotypes, and their electrophysiology is comparable to their wild-type37-39. However, these Tdp1-/- mice do develop age-dependent progressive cerebellar atrophy, and display one of the non-neuronal related SCAN1 symptoms, hypoalbuminemia13,22,39. The Tdp1-/- mice also exhibit an expected hypersensitivity to camptothecin (CPT) or topotecan treatment (a FDA approved camptothecin chemotherapeutic) that was evident in proliferating intestinal cells and hematopoietic cells37-39. Moreover, Tdp1-/- fibroblast extracts show a deficiency in their ability to process 3’phospho-glycolate adducts within double-stranded DNA breaks but not single-strand breaks, and these cells show an increased bleomycin sensitivity37,38.
On the other hand, Mckinnon and coworkers reported that TDP1 and ATM are critical during the development of neuronal cells to control TOPO1 induced DNA damage (40). Mice can survive the individual inactivation of ATM or TDP1; however, dual inactivation causes synthetic lethality. The Atm-/-,Tdp1-/- combination showed to be embryonically lethal between E13.5 and E16.5, a period in which the TOPO1-cc levels are at their maximum40. TOPO1 can be trapped onto the DNA by endogenous DNA lesions, such as abasic sites and single-strand nicks which can occur due to oxidative damage41,42. Indeed, Tdp1-/- and Atm-/- mice show elevated levels of TOPO1-cc in cortical/cerebella tissue during embryonic development up to one year after birth, while control cells or other tissue in the knockout mice show no or minor levels of TOPO1-cc40. This suggests that during development TOPO1-cc lesions accumulated specifically in the neuronal tissue and that for a normal homeostasis ATM and TDP1 regulation of processing stalled TOPO1-cc is critical.
The accumulation of TOPO1-cc and single-strand DNA breaks in the ATM-/- and Tdp1-/- quiescent primary astrocytes is even more pronounced after camptothecin (CPT), ionizing radiation, or hydrogen peroxide treatment. ATM’s response to TOPO1-cc in neuronal cells is independent of its kinase activity or other canonical functions. Inactivation of MRE11, DNA-PKcs, or LIG4 in combination with Tdp1-/- exhibits a normal Mendelian offspring distribution without an obvious phenotype40. However, inactivation of XRCC1 [the scaffold protein within the base excision repair (BER) pathway, which partners include TDP143] showed elevated levels of TOPO1-cc similar to Atm inactivation that are lower than Tdp1 inactivation. Inactivation of Xrcc1 did not reduce the protein levels of TDP1 or other BER affiliated proteins, while the combination of Atm and Xrcc1 inactivation accumulates TOPO1-cc levels similar to Tdp1 inactivation. In an effort to identify the non-canonical function of ATM, Katyal et al observed that ATM is able to regulate post-translational modification (PTM) of TOPO1 by SUMOylation of TOPO1 and ubiquitination via a yet unknown pathway40. These ATM stimulated PTMs in response to CPT treatment, stimulate proteasome-mediated degradation of TOPO1 which was prevented by proteasome inhibitor MG132. The response was lost in A-T cells but still active after treatment with an ATM inhibitor, suggesting that ATM kinase activity is not involved in this response.
In conclusion, both ATM and TDP1 play a critical protective role during neuronal development to prevent accumulation of TOPO1-cc (Figure 2). ATM protects neuronal cells via a novel non-canonical activity, which does not require ATM kinase function. ATM regulates posttranscriptional modification of TOPO1 and potentially TOPO1-cc by stimulating SUMOylation, followed by ubiquitination that promotes proteasome-mediated TOPO1 degradation (Figure 2). Although no SUMO E3-ligases or ubiquitin E2-conjugation/E3-ligase complexes have been identified, in yeast two potential complexes were identified. First is the SUMO ligase Pli1 mediates SUMO modification of TOPO1 while the SUMO-targeted ubiquitin ligase Slx8 was shown to mediate ubiquitin modification44. The second complex is the DNA-, SUMO- and ubiquitin-dependent metalloprotease complex WSS1/CDC48/DOA1 might be responsible for the degradation of modified TOPO1-cc45. The WSS1 human analog is Spartan/DVC1 protein. TDP1, on the other hand, hydrolyzes the 3’phospho-tyrosyl linkage that covalently attaches full length TOPO1 with the 3’phosphoryl end of a DNA strand or the protease resistant TOPO1-peptide1,11. Thus, TDP1 plays a critical role in removal of a protein/peptide-DNA adduct during neuronal development (Figure 2). These studies suggest a potential molecular basis for the etiology of SCAN1; not only TOPO1-cc are accumulating during embryonic development but they are replaced by TDP1H493R-cc, which together maximizes the ability of ATM and the other repair pathways to maintain cell viability, resulting in a slow but progressive cerebellar atrophy (Figure 2). Moreover, the work of McKinnon and coworkers40 gave the first clue, specific accumulation of TOPO1-cc in the neuronal cells, of why the cerebellar is specifically affected and not other tissues.
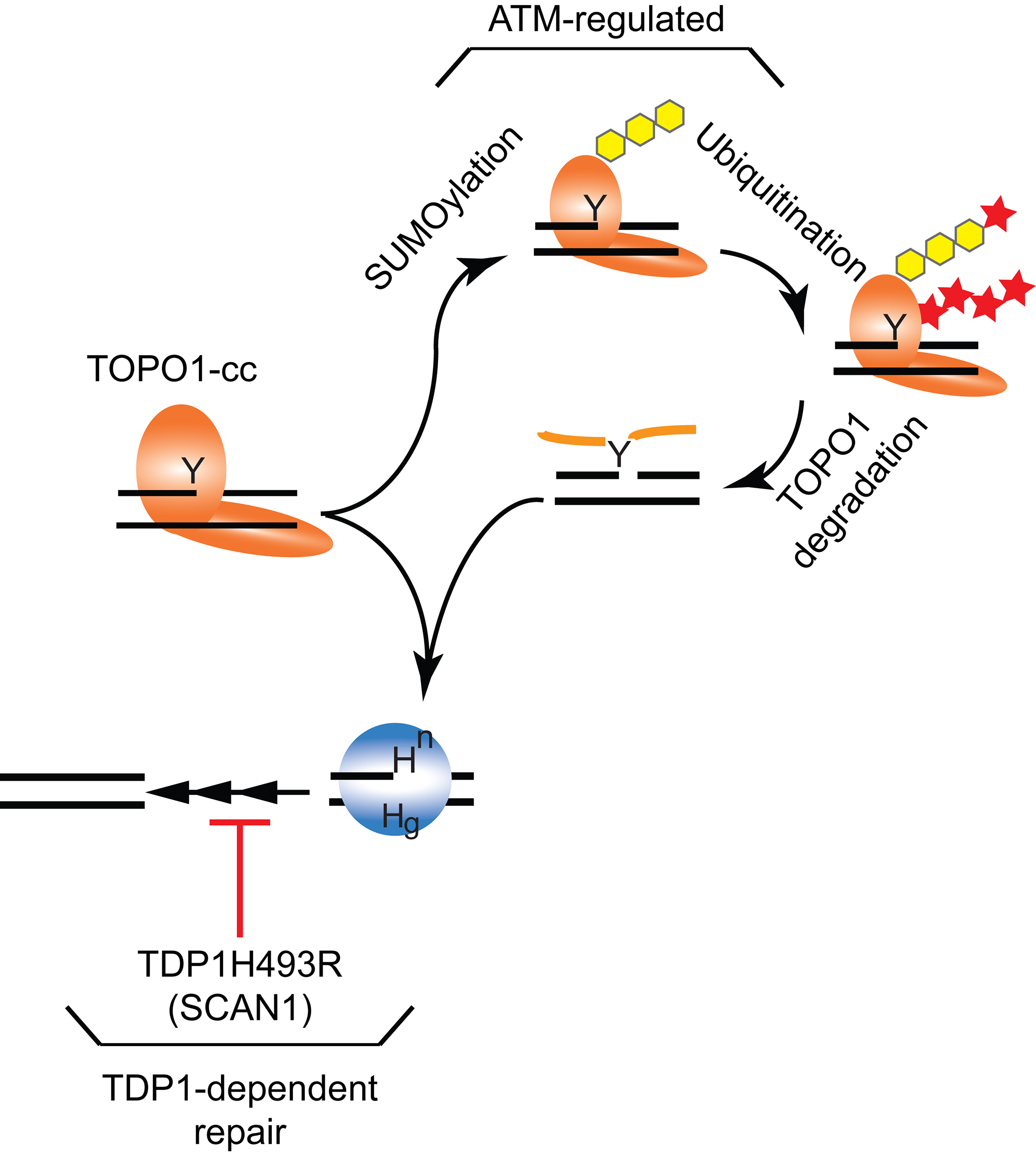
Figure 2: TOPO1-cc processing by TDP1 and ATM independent pathways in neuronal cells. The removal of accumulated TOPO1-cc in neuronal cells during development by noncanonical ATM-regulated SUMOylated (yellow hexagon) followed by ubiquitination (red star) of TOPO1 that results in TOPO1 degradation potentially proteasome-mediated40 or by SUMO stimulated selective ESCRT vesicle-trafficking mediated autophagy47. The protease-resistant covalently linked TOPO1-peptide and, independent of ATM, TOPO1-cc can be directly removed by TDP1-mediated hydrolysis. In SCAN1 patients, the TDP1H493R mutant enzyme will be able to hydrolyze both TOPO1-cc and the TOPO1-peptide fragment from the DNA but will form a stable TDP1H493R-cc11,13,31-33. The accumulated TDP1H493R-cc together with the TOPO1-cc or TOPO1-peptite-DNA complex will maximally challenge the ATM and other DNA repair pathways, resulting in slow progressive cerebellar atrophy.
Acknowledgements
I would like to thank past and current van Waardenburg lab-members and collaborators for inspiring discussions that contribute to increase our knowledge of TDP1 function and Ms. Lisa Park for proofreading and edits. My apologies to the colleagues whom work I could not discuss due to the size limitations. RCAMvW greatly appreciates the financial support from the Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology, the Alabama Drug Discovery Alliance, UAB ACS-IRG Junior Faculty Development Grant (ACS-IRG-60-001-53), the UAB CCC Faculty Development Grant (Cancer Center Core Support Grant P30CA013148), and DOD OCRP pilot award W81XWH-15-1-0198.
References
- Interthal H, Pouliot JJ, Champoux JJ. The tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase Tdp1 is a member of the phospholipase D superfamily. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2001;98(21):12009-14.
- Pouliot JJ, Yao KC, Robertson CA, Nash HA. Yeast gene for a Tyr-DNA phosphodiesterase that repairs topoisomerase I complexes. Science. 1999;286(5439):552-5.
- Yang SW, Burgin AB, Jr., Huizenga BN, Robertson CA, Yao KC, Nash HA. A eukaryotic enzyme that can disjoin dead-end covalent complexes between DNA and type I topoisomerases. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 1996;93(21):11534-9.
- Fam HK, Chowdhury MK, Walton C, Choi K, Boerkoel CF, Hendson G. Expression profile and mitochondrial colocalization of Tdp1 in peripheral human tissues. Journal of molecular histology. 2013.
- Das BB, Dexheimer TS, Maddali K, Pommier Y. Role of tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase (TDP1) in mitochondria. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2010;107(46):19790-5.
- Comeaux EQ, van Waardenburg RC. Tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase I resolves both naturally and chemically induced DNA adducts and its potential as a therapeutic target. Drug Metab Rev. 2014;46(4):494-507.
- Pommier Y, Huang SY, Gao R, Das BB, Murai J, Marchand C. Tyrosyl-DNA-phosphodiesterases (TDP1 and TDP2). DNA repair. 2014;19:114-29.
- Champoux JJ. DNA topoisomerases: structure, function, and mechanism. Annual review of biochemistry. 2001;70:369-413.
- Pommier Y. Drugging topoisomerases: lessons and challenges. ACS chemical biology. 2013;8(1):82-95.
- Wang JC. Cellular roles of DNA topoisomerases: a molecular perspective. Nature reviews Molecular cell biology. 2002;3(6):430-40.
- He X, van Waardenburg RC, Babaoglu K, Price AC, Nitiss KC, Nitiss JL, et al. Mutation of a conserved active site residue converts tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase I into a DNA topoisomerase I-dependent poison. Journal of molecular biology. 2007;372(4):1070-81.
- Interthal H, Chen HJ, Champoux JJ. Human Tdp1 cleaves a broad spectrum of substrates, including phosphoamide linkages. The Journal of biological chemistry. 2005;280(43):36518-28.
- Takashima H, Boerkoel CF, John J, Saifi GM, Salih MA, Armstrong D, et al. Mutation of TDP1, encoding a topoisomerase I-dependent DNA damage repair enzyme, in spinocerebellar ataxia with axonal neuropathy. Nature genetics. 2002;32(2):267-72.
- Barthelmes HU, Habermeyer M, Christensen MO, Mielke C, Interthal H, Pouliot JJ, et al. TDP1 overexpression in human cells counteracts DNA damage mediated by topoisomerases I and II. The Journal of biological chemistry. 2004;279(53):55618-25.
- Borda MA, Palmitelli M, Veron G, Gonzalez-Cid M, de Campos Nebel M. Tyrosyl-DNA-phosphodiesterase I (TDP1) participates in the removal and repair of stabilized-Top2alpha cleavage complexes in human cells. Mutation research. 2015;781:37-48.
- Cortes Ledesma F, El Khamisy SF, Zuma MC, Osborn K, Caldecott KW. A human 5'-tyrosyl DNA phosphodiesterase that repairs topoisomerase-mediated DNA damage. Nature. 2009;461(7264):674-8.
- Murai J, Huang SY, Das BB, Dexheimer TS, Takeda S, Pommier Y. Tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase 1 (TDP1) repairs DNA damage induced by topoisomerases I and II and base alkylation in vertebrate cells. The Journal of biological chemistry. 2012;287(16):12848-57.
- Nitiss KC, Malik M, He X, White SW, Nitiss JL. Tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase (Tdp1) participates in the repair of Top2-mediated DNA damage. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2006;103(24):8953-8.
- Raymond AC, Rideout MC, Staker B, Hjerrild K, Burgin AB, Jr. Analysis of human tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase I catalytic residues. Journal of molecular biology. 2004;338(5):895-906.
- Lavin MF. Ataxia-telangiectasia: from a rare disorder to a paradigm for cell signalling and cancer. Nature reviews Molecular cell biology. 2008;9(10):759-69.
- Caldecott KW. DNA single-strand break repair and spinocerebellar ataxia. Cell. 2003;112(1):7-10.
- Fam HK, Salih MAM, Takashima H, Boerkoel CF. Spinocerebellar Ataxia with Axonal Neuropathy, Autosomal Recessive. In: Pagon RA, Adam MP, Bird TD, Dolan CR, Fong CT, Stephens K, editors. GeneReviews. Seattle (WA)1993.
- Lee Y, McKinnon PJ. Responding to DNA double strand breaks in the nervous system. Neuroscience. 2007;145(4):1365-74.
- Shiloh Y, Ziv Y. The ATM protein kinase: regulating the cellular response to genotoxic stress, and more. Nature reviews Molecular cell biology. 2013;14(4):197-210.
- Ahel I, Rass U, El-Khamisy SF, Katyal S, Clements PM, McKinnon PJ, et al. The neurodegenerative disease protein aprataxin resolves abortive DNA ligation intermediates. Nature. 2006;443(7112):713-6.
- Bras J, Alonso I, Barbot C, Costa MM, Darwent L, Orme T, et al. Mutations in PNKP cause recessive ataxia with oculomotor apraxia type 4. Am J Hum Genet. 2015;96(3):474-9.
- Dumitrache LC, McKinnon PJ. Polynucleotide kinase-phosphatase (PNKP) mutations and neurologic disease. Mech Ageing Dev. 2016.
- Paucar M, Malmgren H, Taylor M, Reynolds JJ, Svenningsson P, Press R, et al. Expanding the ataxia with oculomotor apraxia type 4 phenotype. Neurol Genet. 2016;2(1):e49.
- Gomez-Herreros F, Schuurs-Hoeijmakers JH, McCormack M, Greally MT, Rulten S, Romero-Granados R, et al. TDP2 protects transcription from abortive topoisomerase activity and is required for normal neural function. Nature genetics. 2014;46(5):516-21.
- McKinnon PJ. TDP2 keeps the brain healthy. Nature genetics. 2014;46(5):419-21.
- El-Khamisy SF, Saifi GM, Weinfeld M, Johansson F, Helleday T, Lupski JR, et al. Defective DNA single-strand break repair in spinocerebellar ataxia with axonal neuropathy-1. Nature. 2005;434(7029):108-13.
- Gajewski S, Comeaux EQ, Jafari N, Bharatham N, Bashford D, White SW, et al. Analysis of the active-site mechanism of tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase I: a member of the phospholipase D superfamily. Journal of molecular biology. 2012;415(4):741-58.
- Interthal H, Chen HJ, Kehl-Fie TE, Zotzmann J, Leppard JB, Champoux JJ. SCAN1 mutant Tdp1 accumulates the enzyme--DNA intermediate and causes camptothecin hypersensitivity. The EMBO journal. 2005;24(12):2224-33.
- Comeaux EQ, Cuya SM, Kojima K, Jafari N, Wanzeck KC, Mobley JA, et al. Tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase I catalytic mutants reveal an alternative nucleophile that can catalyze substrate cleavage. The Journal of biological chemistry. 2015;290(10):6203-14.
- Fam HK, Walton C, Mitra SA, Chowdhury M, Osborne N, Choi K, et al. TDP1 and PARP1 deficiency are cytotoxic to rhabdomyosarcoma cells. Molecular cancer research : MCR. 2013;11(10):1179-92.
- Meisenberg C, Gilbert DC, Chalmers A, Haley V, Gollins S, Ward SE, et al. Clinical and cellular roles for TDP1 and TOP1 in modulating colorectal cancer response to irinotecan. Molecular cancer therapeutics. 2015;14(2):575-85.
- Hawkins AJ, Subler MA, Akopiants K, Wiley JL, Taylor SM, Rice AC, et al. In vitro complementation of Tdp1 deficiency indicates a stabilized enzyme-DNA adduct from tyrosyl but not glycolate lesions as a consequence of the SCAN1 mutation. DNA repair. 2009;8(5):654-63.
- Hirano R, Interthal H, Huang C, Nakamura T, Deguchi K, Choi K, et al. Spinocerebellar ataxia with axonal neuropathy: consequence of a Tdp1 recessive neomorphic mutation? The EMBO journal. 2007;26(22):4732-43.
- Katyal S, el-Khamisy SF, Russell HR, Li Y, Ju L, Caldecott KW, et al. TDP1 facilitates chromosomal single-strand break repair in neurons and is neuroprotective in vivo. The EMBO journal. 2007;26(22):4720-31.
- Katyal S, Lee Y, Nitiss KC, Downing SM, Li Y, Shimada M, et al. Aberrant topoisomerase-1 DNA lesions are pathogenic in neurodegenerative genome instability syndromes. Nat Neurosci. 2014;17(6):813-21.
- Pourquier P, Pilon AA, Kohlhagen G, Mazumder A, Sharma A, Pommier Y. Trapping of mammalian topoisomerase I and recombinations induced by damaged DNA containing nicks or gaps. Importance of DNA end phosphorylation and camptothecin effects. The Journal of biological chemistry. 1997;272(42):26441-7.
- Pourquier P, Ueng LM, Fertala J, Wang D, Park HJ, Essigmann JM, et al. Induction of reversible complexes between eukaryotic DNA topoisomerase I and DNA-containing oxidative base damages. 7, 8-dihydro-8-oxoguanine and 5-hydroxycytosine. The Journal of biological chemistry. 1999;274(13):8516-23.
- Plo I, Liao ZY, Barcelo JM, Kohlhagen G, Caldecott KW, Weinfeld M, et al. Association of XRCC1 and tyrosyl DNA phosphodiesterase (Tdp1) for the repair of topoisomerase I-mediated DNA lesions. DNA repair. 2003;2(10):1087-100.
- Steinacher R, Osman F, Lorenz A, Bryer C, Whitby MC. Slx8 removes Pli1-dependent protein-SUMO conjugates including SUMOylated topoisomerase I to promote genome stability. PloS one. 2013;8(8):e71960.
- Balakirev MY, Mullally JE, Favier A, Assard N, Sulpice E, Lindsey DF, et al. Wss1 metalloprotease partners with Cdc48/Doa1 in processing genotoxic SUMO conjugates. Elife. 2015;4.
- Davies DR, Interthal H, Champoux JJ, Hol WG. Crystal structure of a transition state mimic for Tdp1 assembled from vanadate, DNA, and a topoisomerase I-derived peptide. Chemistry & biology. 2003;10(2):139-47.
- Reid RJ, Gonzalez-Barrera S, Sunjevaric I, Alvaro D, Ciccone S, Wagner M, et al. Selective ploidy ablation, a high-throughput plasmid transfer protocol, identifies new genes affecting topoisomerase I-induced DNA damage. Genome Res. 2011;21(3):477-86.
